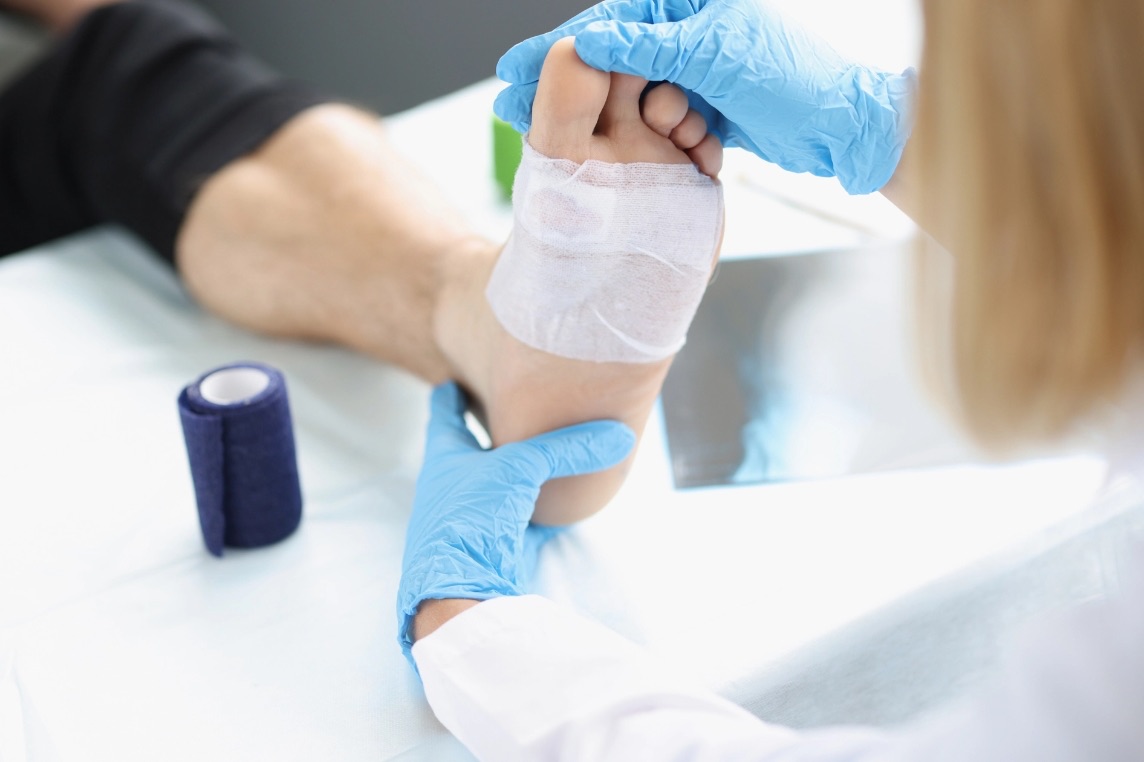
Intra-Articular Hyaluronic Acid Injection
In cases of mild to moderate osteoarthritis, an intra-articular hyaluronic acid injection fills the joint with a viscous compound similar to synovial fluid, enabling proper movement. Hyaluronic acid also has anti-inflammatory properties, thus reducing the need for analgesics and corticosteroïds.
Related Pathology

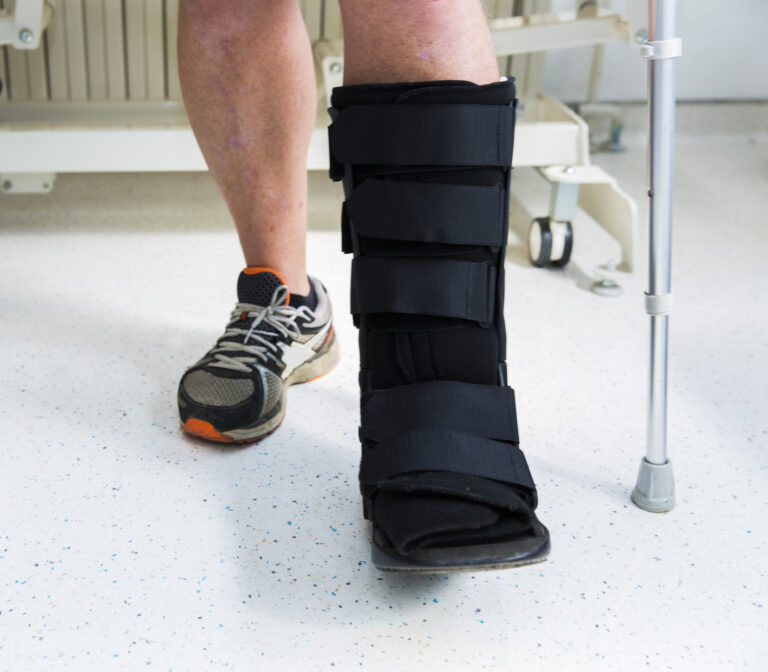
Offloading Boot
When strict immobilization is necessary during the healing process, an offloading boot can accelerate healing for fractures, grade 3 ligament sprains, and following procedures with a risk of prejudice without immobilization.
Related Pathology
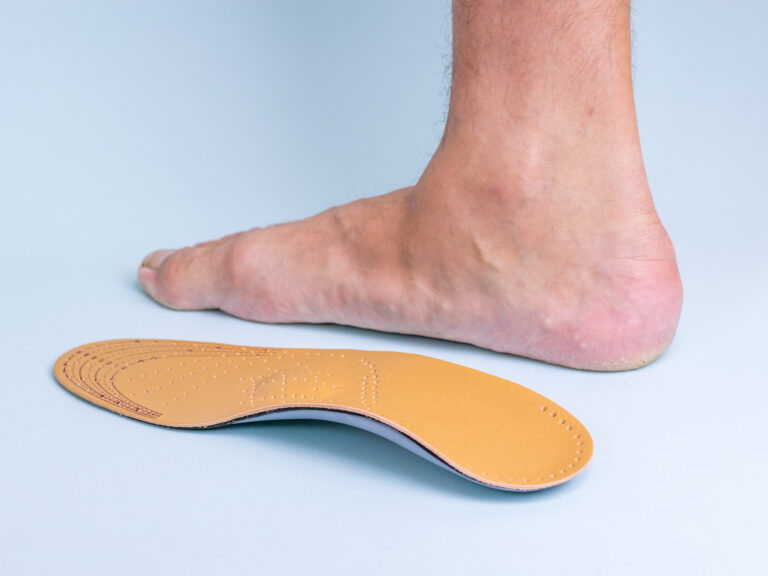
Plantar Orthotics
Plantar orthotics are orthopaedic supports inserted into shoes that modify foot and ankle segment position and movement during walking and physical activities. A therapeutic effect can be achieved at different stages of a pathology and in preventing mechanical disorders.
Related Pathologies
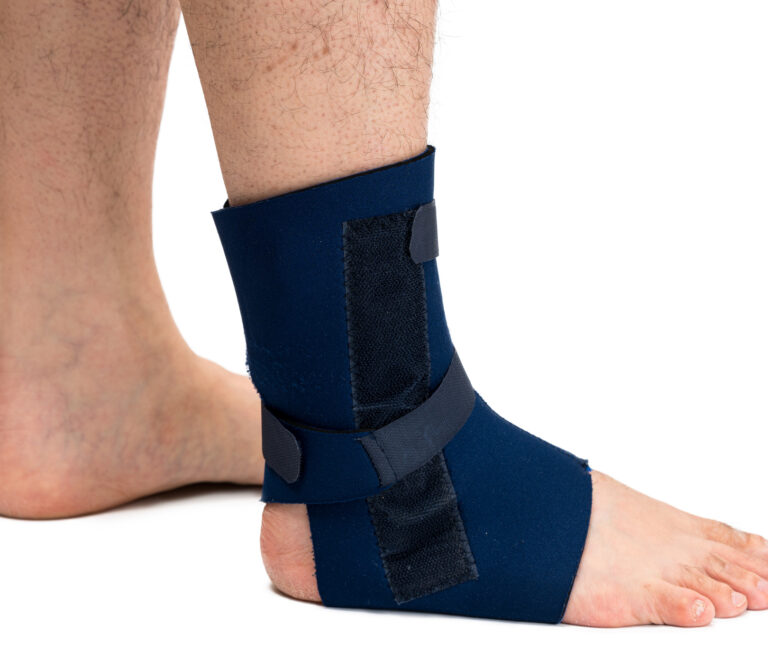
Orthopaedic Supports
In cases of mechanical disorders, acute and chronic injuries, and when dermatological lesions cause pain, orthopedic supports help redistribute weight and modify foot and ankle behavior during walking or physical activities. Most commonly used orthopaedic devices are plantar orthotics and offloading boots.
Related Pathology
Personalized Exercise Program
The body has the ability to heal itself. By being proactive and by progressively stimulating the body, necessary adaptations can occur safely. Additionally, an exercise program helps reduce the recurrence of common injuries.
Related Pathologies

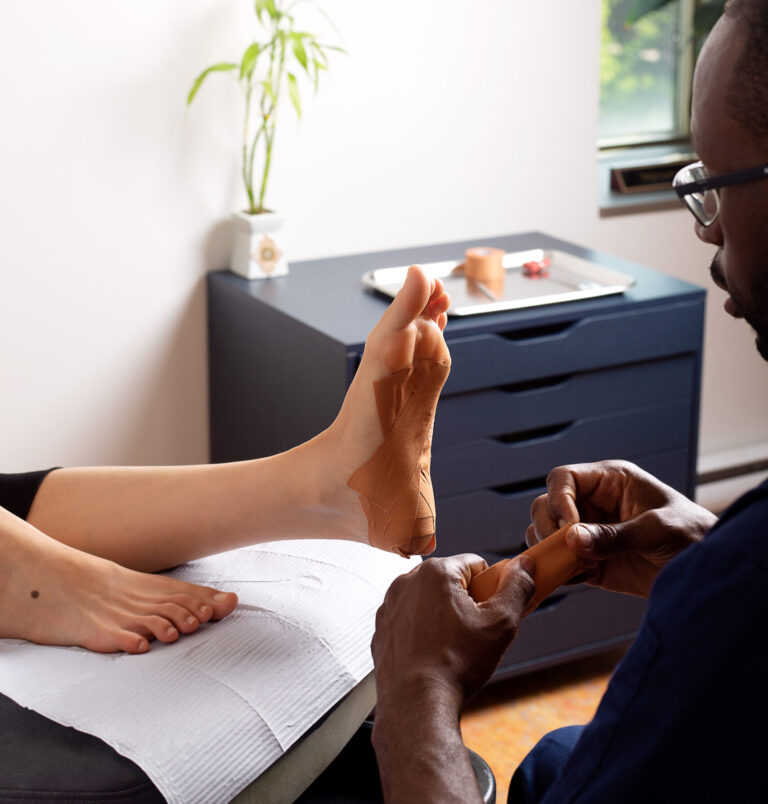
Therapeutic Bandages
When injured, it’s essential to protect the structure to prevent aggravation. In chronic injuries, bandages can help avoid worsening the condition and assist in restoring proper function. Bandages can also stimulate sensitivity, proprioception, and provide a sense of security during activities. In some cases, they help confirm a diagnosis.
Related Pathologies

Peritendinous Hyaluronic Acid Injection
Peritendinous hyaluronic acid injection is a procedure where hyaluronic acid is injected around the tendons. This aims to reduce pain and improve mobility in conditions such chronic tendinopathy. Hyaluronic acid helps lubricate the tendons and reduce inflammation. It is often used when more conservative treatments are not sufficient.
Related Pathologies

Ingrown toenail surgery
An ingrown toenail results from a conflict between the edge of a nail and the surrounding skin. Increased nail curvature, poor nail cutting or trauma can create an injury that causes the problem. To remedy the issue, we can perform ingrown toenail surgery or permanent matricectomy under local anesthesia. The offending edge is cut and the nail matrix tissues are denatured so they can no longer regenerate, leaving a nail that is slightly slimmer and less likely to create conflict with the surrounding skin.
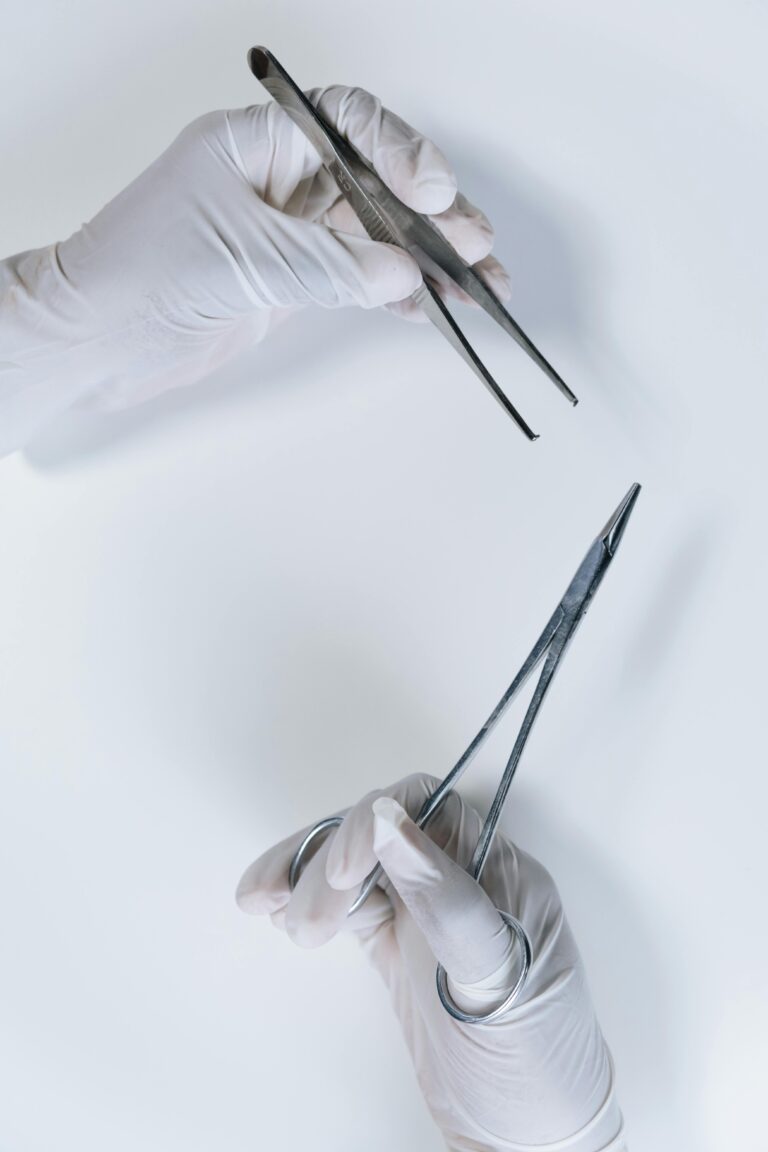
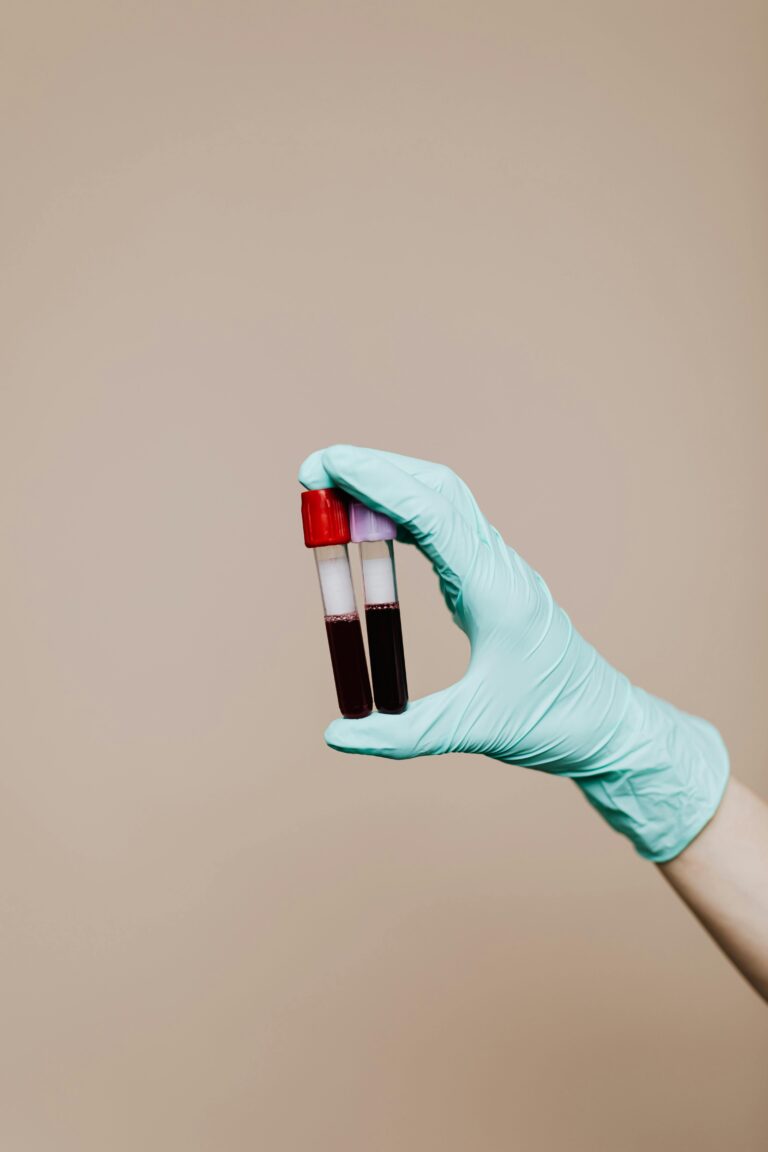
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP)
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a treatment used for chronic musculoskeletal conditions and injuries that are refractory to conservative treatment, such as the application of ice, bandages, non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, cortisone, and orthotics. and osteoarthritis. For example, PRP can be used in the treatment of chronic Achilles tendinopathy, plantar fasciopathy, mild to moderate osteoarthritis of the big toe, and in the treatment of stable osteochondral lesions.
The procedure involves collecting a blood sample from the patient. Then, the blood is centrifuged to separate the red blood cells from the plasma. The plasma, rich in platelets containing growth factors and other inflammatory mediators, is administered to the pathological site, allowing the restoration of the inflammatory cascade to reorganize cellular repair.
Related Pathologies
Shockwave Therapy
The principle behind this technique is to send low-energy waves to cause tiny internal lesions that awaken the metabolism’s response to these microaggressions. Blood circulation will be improved, calcium deposits will break down and the body will produce the necessary substances, such as collagen, which are useful for the regeneration and healing of tissues.
Related Pathologies
Manual Therapy
The goal of manual therapy is to restore proper joint movement, and achieve optimal function by reducing restrictions in joint mobility. Following trauma such as sprains or even prolonged immobilization, tissues adapt to a poor position. Using the hands, small or large amplitude movements can stimulate the reorganization of collagen fibers as well as the movement of joint fluid. Therapeutic taping is most often applied afterward to ensure a prolonged effect.
Related Pathologies